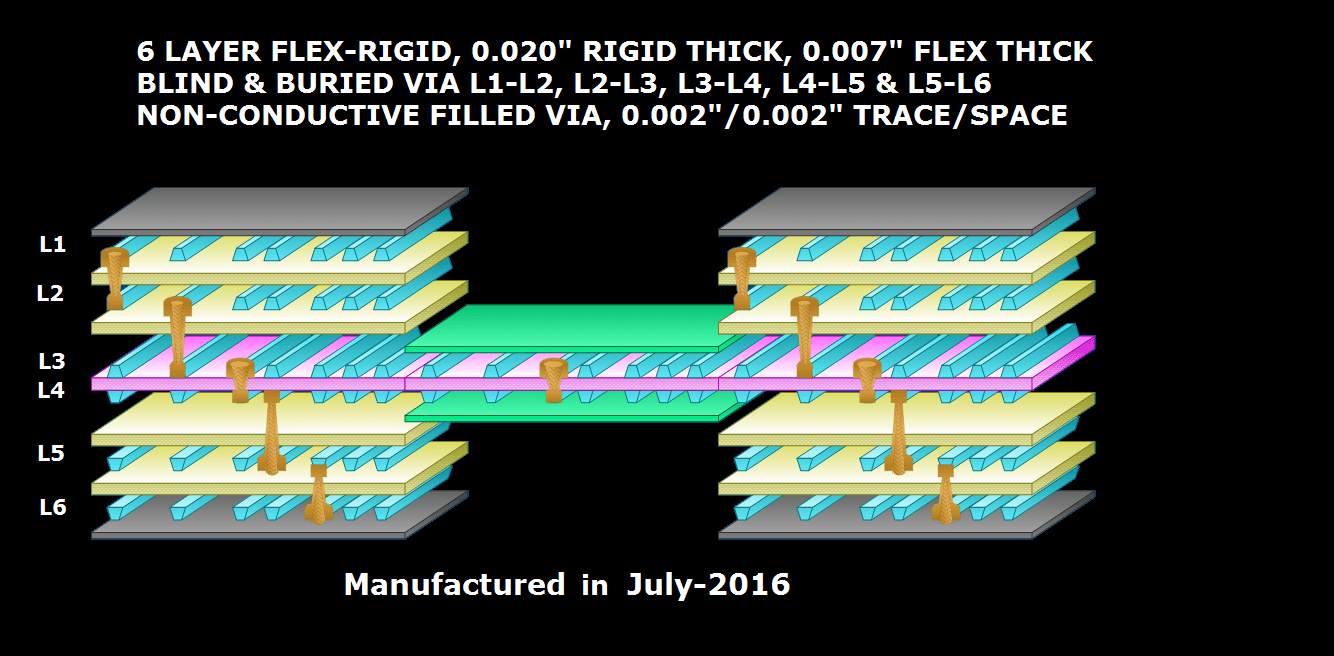
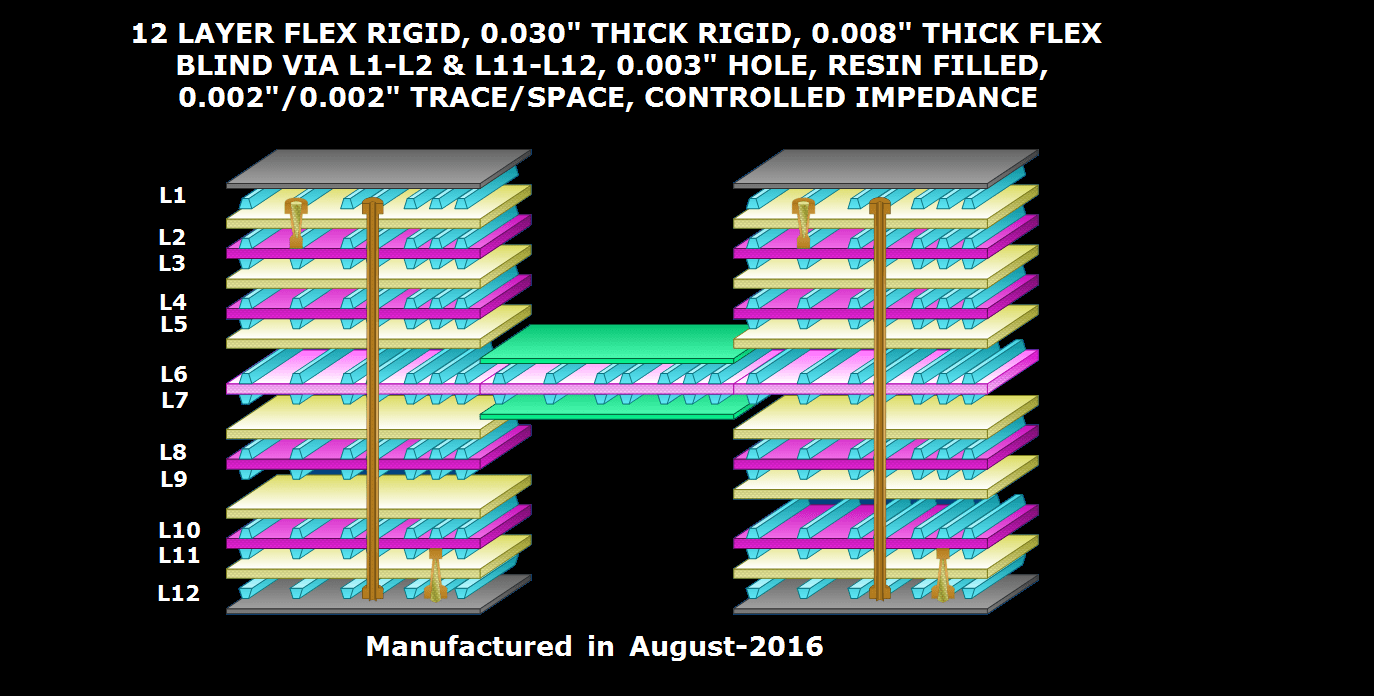
Manufacturing MCPCBs at Rush Flex PCB
Layers and Bonding
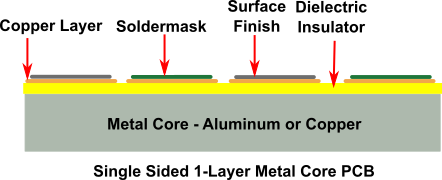
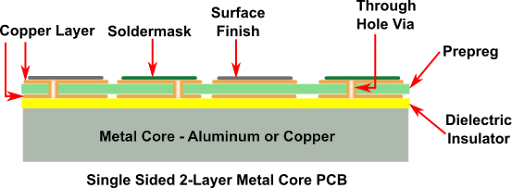
For a typical single-sided 1-layer MCPCB, we first bond the circuit layer of copper foil to the thermally conducting dielectric material layer. Then we bind the dielectric layer to the metal core.
The metal core in the MCPCB is the thickest material on the board. Thus, its thickness depends on the requirements of the application.
Typically, the thicknesses of the metal core we offer are 1, 1.5, and 3.2 mm. Apart from dissipating heat, the metal layer offers rigidity to the circuit, maintains it flat, and provides adequate thickness to make the circuit compatible with the mounting hardware. However, we do not coat the exposed metal side of the board with anything like a solder mask or surface finish.
While the dielectric thickness is around 100 µm, the copper foil thickness is typically 1 oz to 10 oz. The main function of the thermally conducting dielectric material layer is to isolate the copper circuit layer from the metal layer while assisting in heat transfer between them.
The dielectric layer effectively disperses the heat from the components to the metal core. Although the higher the thermal conductivity of the dielectric layer, the better will be the heat transfer, but the cost will also increase.
Plated-Through Holes
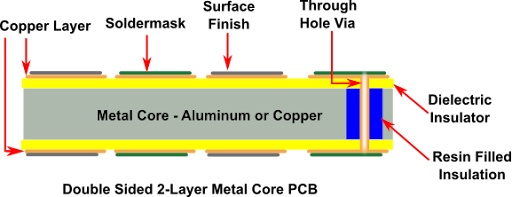
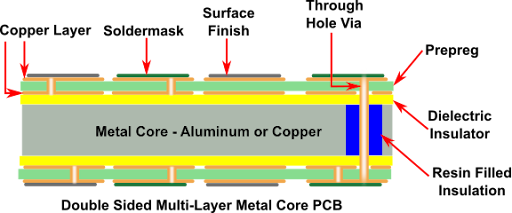
Rush Flex PCB recommends minimizing the use of components requiring plated through holes. This is because the bottom layer being metal, PTH, or NPTH with conductive component leads inserted into it will lead to an electrical short. If PTH components are unavoidable, they must be isolated from the metal core.
We achieve this by drilling the metal core approximately 40-50 mils larger than the PTH dia. Later, we fill them with non-conductive epoxy fillers and then press them.
Once pressing is over, we remove the filler compound from the surface and prepare the boards for lamination with the inner layer cores. After lamination, we drill the plated through holes and the rest of the process is standard.
Typically, regular LED PCBs typically require via-in-pads for proper heat dissipation. This calls for an additional drilling process, making the task more complicated.
Our MCPCBs, with their higher capacity for heat dissipation, do not require via-in-pads, making the manufacturing process simpler.
Stackup in MCPCBs
Lastly, In our double sided pcb and multi-layer MCPCBs, we maintain a symmetrical stackup on either side of the metal core. The number of layers on the top of the core is equal to the layers on the bottom. Moreover, to avoid warpage issues, we also prefer to maintain copper symmetry just as we do in our standard printed circuit boards.